It’s a scary, potentially deadly communicable disease, and it could be coming soon to your neighborhood, school or workplace.
But unlike Ebola, which has been commanding worldwide media attention in recent weeks, influenza can be prevented with an effective, widely-available tool that you can get even at the corner drug store or supermarket.
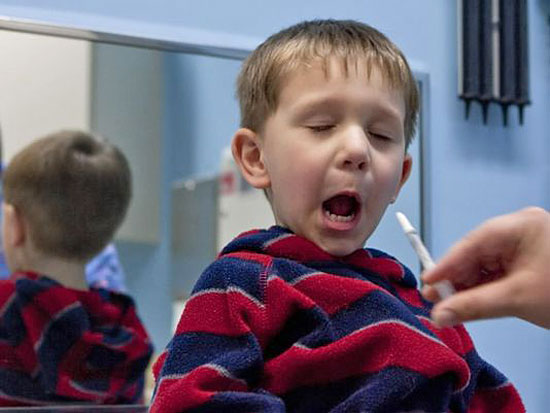
We’re talking, of course, about the good old annual flu shot—which is being promoted in more varieties than ever this year, from nasal spray for kids to high dosages for seniors to vaccines that include an extra strain of virus for good measure.
With Ebola fears running high, county Department of Public Health officials are making a special push to persuade people to get immunized early in the season—whichever type of vaccination they choose—so that they don’t come down with the flu. Since flu can have some Ebola-like symptoms (including fever) it makes sense to minimize the number of people who get it and then head to the emergency room fearing the worst.
In other words, flu vaccinations may be an easier sell this season than they have been in years past.
The Ebola situation has created a “teachable moment,” said Michelle Parra, the director of Public Health’s immunization program. She said it is a chance to drive home the message that flu can be serious and even fatal, especially to those with underlying medical conditions or overall frail health.
Ebola has killed thousands in Africa, but at this point only two people are believed to have contracted the disease in the United States—both of them nurses who treated Thomas Eric Duncan, who was infected with the disease in Liberia and later died from it at a hospital in Texas. Flu, on the other hand, claims the lives of tens of thousands of Americans each year—up to 49,000 annually, according to the Centers for Disease Control. Those stricken include the 105 Los Angeles County residents—101 adults and four children— who died during the last flu season in 2013-14. That was the highest death toll in the county since the H1N1 pandemic of 2009-10, when 127 died.
No deaths and only “sporadic” flu activity have been reported to L.A. County so far this season, which officially runs from November 1 to March 31. But the county Department of Public Health emphasizes that it’s important to get the vaccine early, since it takes about two weeks to take full effect against flu viruses.
While the overall message is to get the vaccine, period, and as soon as possible, a number of new choices have been cropping up—giving consumers a robust array of options to talk over with their health care providers.
One is the first official recommendation that children aged 2 to 8 get nasal spray instead of a shot, unless they have a condition like asthma. The nasal mist also can be given to adults up to the age of 49.
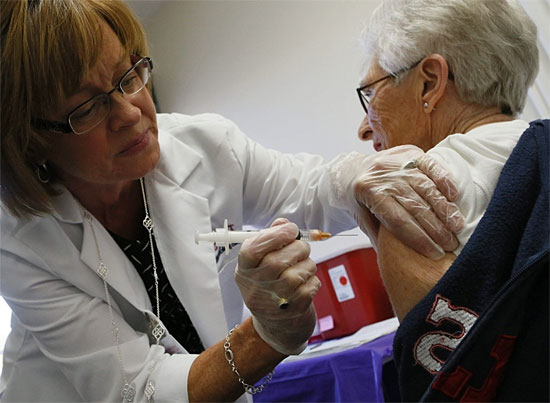
Then there’s the high-dose vaccine for people 65 and over, which, according to a study recently reported in the New England Journal of Medicine, offers more protection for seniors than the traditional vaccine.
Finally, for the second year in a row, there are two different kinds of vaccine blends on the market—one containing three strains of viruses that cause the flu, the other made up of four.
While that’s good news overall (it indicates that manufacturers are becoming increasingly responsive to flu viruses circulating in other parts of the world before they reach the U.S.) it does present a bit of a communications quandary for health officials, according to L.J.Tan, chief strategy officer for the nonprofit Immunization Action Coalition.
That’s because the four-strain, or quadrivalent, vaccine accounts for only about half of the available vaccine. The CDC estimates that 76 million doses of the quadrivalent will be produced this season, while the rest of the 151 to 156 million doses that make up the nation’s total supply will be three-strain, or trivalent.
“We think it’s most important to get vaccinated [with whichever vaccine is most readily available.] We don’t want people going around saying, ‘Oh, the quadrivalent has four, it’s better, therefore I’m going to wait.’ Because by the time they wait it could be too late,” Tan said. “That’s one of the messaging nuances that we’re trying to figure out and get out there.”
Tan said researchers play a guessing game each year as they try to predict the virus strains heading our way in the coming flu season. The so-called B-strains are generally considered less lethal but are harder to predict, so the quadrivalent vaccine doubles down and includes both. The A-strains, meanwhile, are the most deadly, so both the trivalent and quadivalent vaccines include them—and that’s why health officials say it’s better to get a timely shot than to waste too much time shopping around.
In the midst of this expanding universe of vaccine choices, meanwhile, officials warn consumers not to be sidetracked by claims that flu shots give you the very disease you’re trying to avoid. “Flu shots cannot give you flu,” Public Health’s Parra said. “What happens is a lot of time people already have flu in their system” and wrongly attribute it to the vaccination they just received.
Finally, health experts emphasize that we’re all in this together. Even if you don’t feel personally vulnerable, it’s a good idea to get vaccinated to help those who are more susceptible.
“There’s so many people trying to push different messages, and I do think this idea of ‘Do it for your grandma’ is the one the CDC tries to lead with,” said Tan, of the Immunization Action Coalition. “Protect yourself, protect your family.”
More tips from the county Department of Public Health are here.
Posted 10/23/14